Most Atp Is Produced Directly as a Result of
Prepared collected and produced intelligence from publicly available information and open sources to gain knowledge and understanding of foreign lands peoples potential threats and armies. The result of uncoupling electron transport from the phosphorylation of ADP is that a great deal of substrate is oxidized with little production of ATP although heat is produced.
UTP is the source of energy for activating glucose and galactose.
. O 2 provides most of the energy for the process and combines with protons and the electrons to make water. 17 During glycolysis when glucose is catabolized to pyruvate most of the energy of glucose is A transferred to ADP forming ATP. As a result ATP synthase will start hydrolyzing some of the ATP in the matrix until a new balance of ATP to ADP and P i is reached where ΔG ATP synthesis 110 kcalmole and so on.
Oxidative phosphorylation the process by which ATP is synthesized from ADP and inorganic phosphate Pi that takes place in mitochondrion. There are a number of proteins in. Enzymes are protein catalyst produced by a cell and responsible for the high rate and specificity of one or more intracellular or extracellular biochemical reactions.
D ATP traps more energy than is produced in its formation. ATP is the most commonly used source but GTP is used in protein synthesis as well as a few other reactions. AMP is part of the structure of some of the coenzymes like.
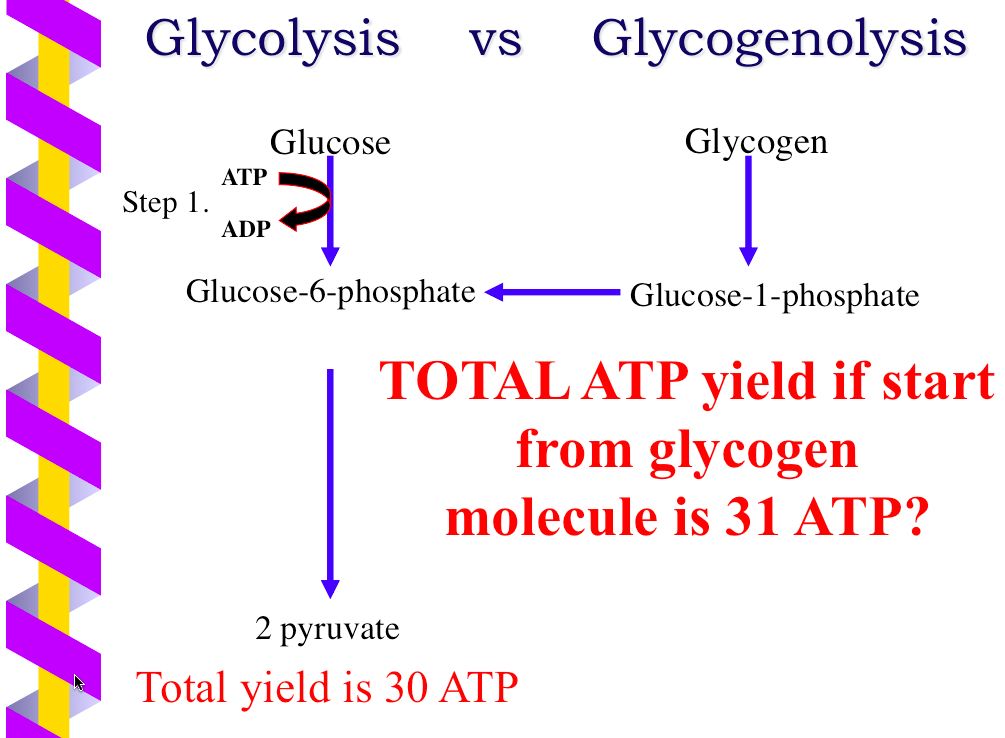
ATP is known as the energy currency of the cell because ____. Of ATP is needed to drive this pathway but four molecules of ATP are eventually formed for a net gain of 2 ATP. Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway that takes place in the.
The substance upon which an enzyme. C retained in the pyruvate. Open sources possess much of the information needed to understand the.
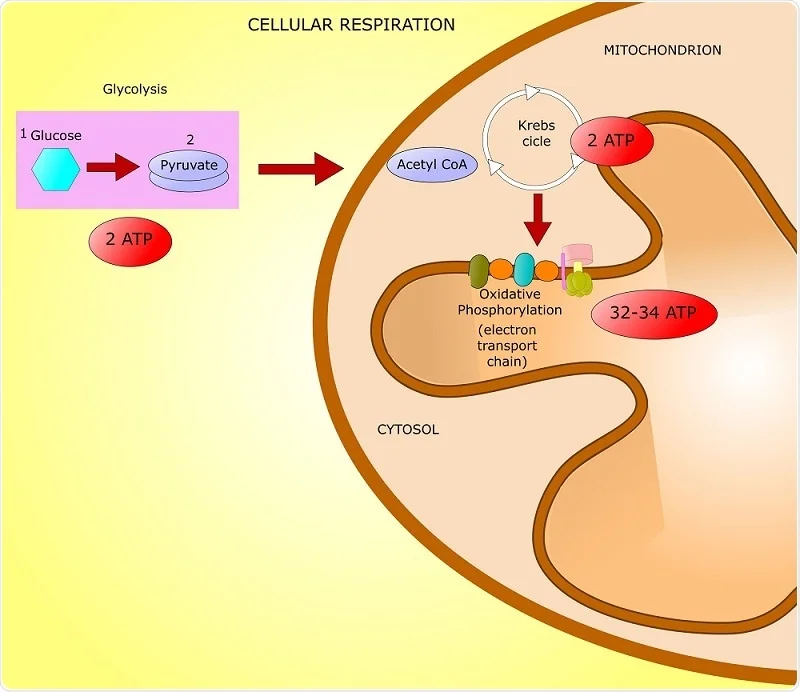
Glucose is a simple sugar with the molecular formula C 6 H 12 O 6Glucose is the most abundant monosaccharide a subcategory of carbohydratesGlucose is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide using energy from sunlight where it is used to make cellulose in cell walls the most abundant carbohydrate in the world. During anaerobic conditions such as what occurs in muscles during a burst of extreme activity when oxygen is not obtained fast. Most of the ATP produced by aerobic cellular respiration is made by oxidative.
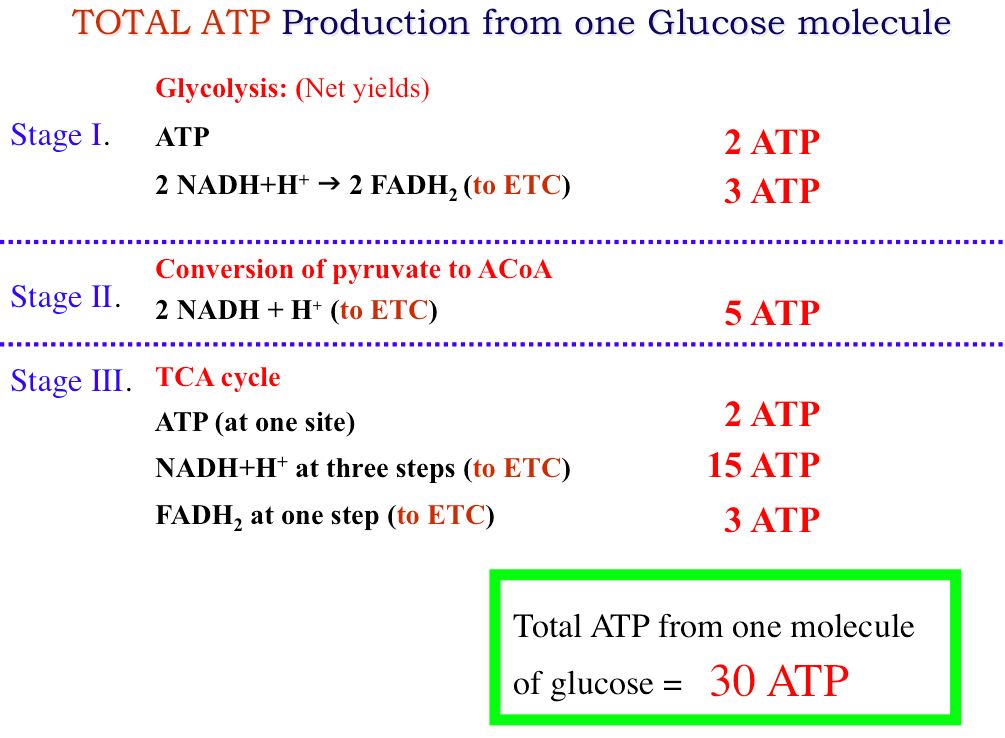
There are two mechanisms of ATP synthesis. Enzymes are biological catalysts responsible for supporting almost all of the chemical reactions that maintain animal homeostasis. Partial oxidation of glucose produces energy in the form of ATP a net gain of 2 ATP and two molecules of NADH a cellular coenzyme used during metabolism.
Lastly ATP leaves through the ATP channel and out of the mitochondria. This is one of the physiological mechanisms for heat production to maintain body temperature without performing physical work non-shivering thermogenesis. 2 ATP from Glycolysis 4 produced 2ATP used up 2 ATP from Glycolysis 4 produced 2ATP used up This goes back to what I was saying about there not being a set amount of ATP produced per NADHFADH2 molecule different sources will quote different amounts.
During glycolysis glucose ends up as two molecules of pyruvate. The released hydrogen ions make ADP for an result of 32 ATP. B ATP passes energy along in an electron transport chain.
A ATP is the most readily usable form of energy for cells. ATP synthetases are the most important universal secondary energy transducers integrated into plasma membranes. E only eukaryotic cells use this energy currency.
Functionally the ATP synthases are reversible ion-transporting ATPases driving the reaction ADP Pi ATP H 2 O by dissipation of a ΔμH or ΔμNa. Enzyme reactions are always reversible. ATZS-CDI-D ATP 2-229 550 Cibeque Street Fort Huachuca.
The mark schemes word is final. B transferred directly to ATP. CTP is an energy source in lipid metabolism.
Two molecules of ATP two of NADH that could directly feed into the respiratory chain and two of pyruvate. The latter enters the TCA cycle and undergoes complete oxidation in aerobic conditions. E used to phosphorylate fructose to form fructose-6-phosphate.
Bacterial ATP synthetases and those of mitochondria and chloroplasts are of the F 0 F 1-type. Most of them not just ATP are the sources of energy that drive most of our reactions. D stored in the NADH produced.
In many bacteria ATP synthase is routinely reversed in a transition between aerobic and anaerobic metabolism as we shall see later. C ATP energy is passed to NADPH. The most commonly accepted amount is as I said 3 ATP per NADH.
The final balance of this process is then.

Atp Production From Food Metabolism Amino Acids Monosaccharides And Download Scientific Diagram

Adenosine Triphosphate Definition Structure Function Facts Britannica

Cellular Respiration Biochemistry Teaching Biology Biology Lessons
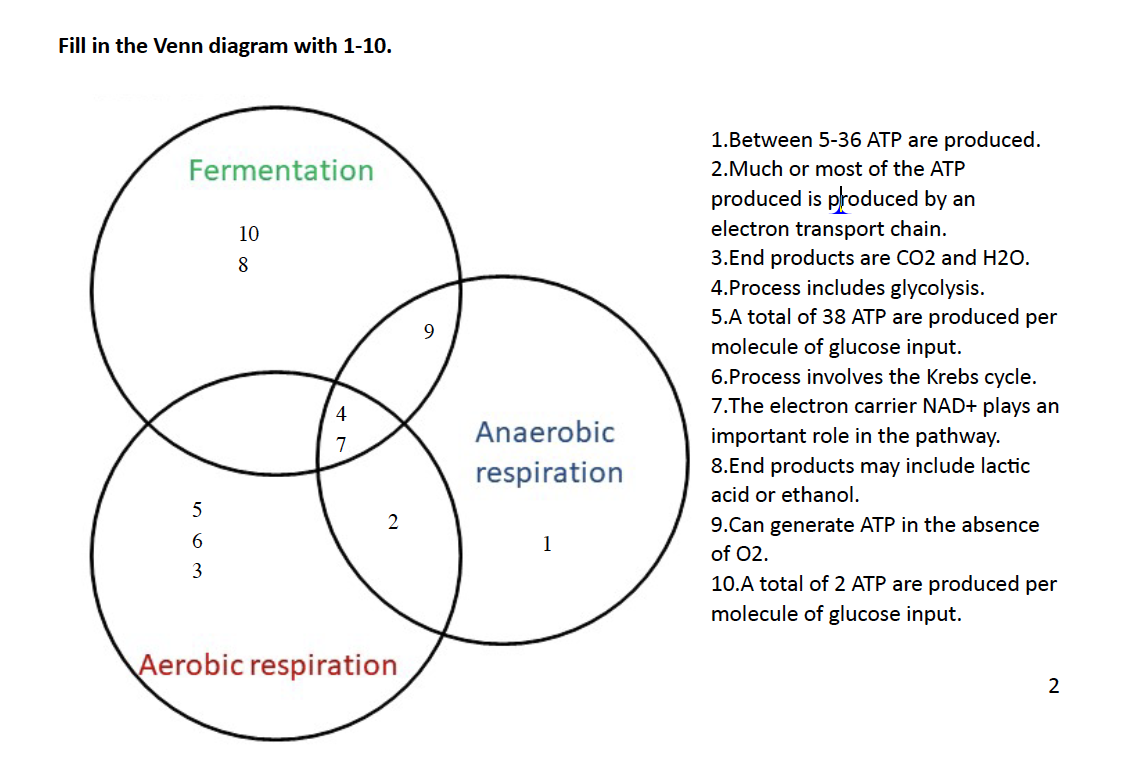
Solved Fill In The Venn Diagram With 1 10 Fermentation 10 8 Chegg Com

34 2b Food Energy And Atp Biology Libretexts

Cellular Respiration Why Is Atp Produced In Photosynthesis Used To Synthesize Glucose Biology Stack Exchange

24 2 Carbohydrate Metabolism Anatomy And Physiology Physiology Anatomy And Physiology Anaerobic Respiration

Cellular Respiration Definition Equation Cycle Process Reactants Products Britannica
How Much Atp Is In The Glycolysis Cycle Quora

Yeast Energy Metabolism Yeasts Have Two Pathways For Atp Production Download Scientific Diagram
How Much Atp Is Produced During One Round Of A Krebs Cycle Quora

Electron Transport Chain Biochemistry Electron Transport Chain Microbiology

Cellular Respiration Review Article Khan Academy

The Whys And Hows Of Calculating Total Cellular Atp Production Rate Trends In Endocrinology Metabolism

Khan Academy Electron Transport Chain Oxidative Phosphorylation Biology


Comments
Post a Comment